View
Views are one of the main components of mobile apps. The main purpose of a view is to display a list of records of a particular entity.
Views are created and managed in Woodford. They are defined within app projects. Each entity has its own views. A single entity can have multiple views.
Types of views
- Public view displays the list of records of an entity.
- Example: A list of your contacts.
- Associated view displays a list of records from an associated entity, that is relevant for the selected item.
- Example: A list of appointments of a particular contact.
- Lookup view displays the list of records of an entity (same as public view), however, it is used when user should select an entity to be inserted into a form.
- Dashboard view is a combination of multiple views and charts.
| Note | If a custom associated view, lookup view, or dashboard view does not exist, the public view is used instead. |
Managing views
Views are associated with an entity. To see a list of views for an entity, edit an app project, select the entity and click Show UI.
On the Mobile Views, Forms and Charts screen, you can add, clone, or remove views, edit them and change their properties, as well as export them (to a file in XML format) or import them (for example, to a different app project).
Creating a view (example)
Create a new public view for the Competitor entity:
- Select the entity in the Project menu and click Show UI.
- Click New View and set the properties of the view:
- Enter a descriptive Name, for example Competitors.
- As Type, select one of the four view types (Public List, Associated List, Lookup List, or Dashboard List). In this example, use Public List.
- In this example, use Primary + 2 Secondary as your Template. You can choose any of the templates or proceed with a blank view, but keep in mind the limited screen size of a mobile device. We recommend to use templates for your new lists; adapting a list is often less work than creating one from scratch.
- Select Hidden if you don't want that your new view is listed as an option in the app to users when they switch views. However, the view can still be used in the app when you design it that way.
- Click OK to start designing your view.
When you edit the properties of an existing view, you can configure additional parameters:
- Default - Make this view the default initial view. If the default is not set, the first view in alphabetical order is used.
- Mode - Make this view dedicated for online or offline view, or for both.
The view designer window is divided into multiple panes:
- Toolbar with buttons on top
- Properties pane on the left shows properties of the selected component in the Designer pane.
- Designer pane in the center shows a schema of a single row of the view. You can use the slider to zoom in or out; or you can use the mouse wheel.
- Fields pane on the right shows fields that you can add to the view.
Click Select Fields to display a list of fields defined for this entity.
- These fields are available for the mobile device, not only for being displayed in the view, but also for sorting and search.
- Fields that you select will be available in the Fields pane. You can also disable fields that need to be enabled for synchronization, but they do not need to be added to View to make the designer tidier.
- If you need additional fields, you must enable them on your entity; see App projects#Managing fields for more information.
If you created your new view as described above, your Designer pane will show three cells: one big cell for Name in the top row and two empty cells below. You have two options how to populate the empty cells with fields (or replace field with another one):
- Select a cell and click Binding on the Properties pane.
- Double-click a cell.
In both cases, you must select from a list of fields. Click OK to confirm your selection.
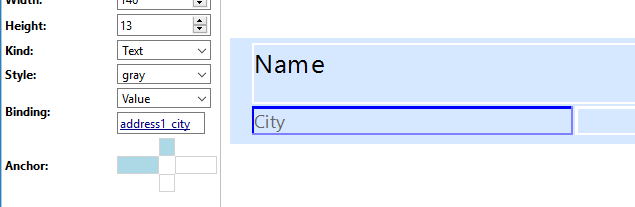
Each field has four available anchors on the Properties pane. Click an anchor to toggle it on and off. Active anchors fix the boundary position of the field to the side the anchor is pointing to. In the case of the picture below, the City field binds to the left border of the view item and to the bottom border of the Name field. When the anchors are set correctly, the view will not be scrambled when users rotate the screen, e.g., from portrait to landscape.
Properties pane
The following properties can be configured on View level:
- Columns:
- Auto Grid
- Auto Header
The following properties can be configured on Row level. First, use the drop-down list to select which row you want to modify.
- Name – Defines the Row’s name (to distinguish between multiple Row designs).
- Width – Defines the width of the row in a view.
- Height – Defines the height of the row in a view.
- Design Size - Allows you to define width and height for different operating systems.
- Color – Defines the color of the row’s background.
- Selected – Defines the color of the row’s background, when the record in view is selected.
- Next Wide
The following properties can be configured on Cell level. First, use the drop-down list to select which cell you want to modify. Alternatively, you can select the cell in the Designer pane.
- Left, Top, Width, Height – Coordinates of the selected element (field on the row). You can adjust the element size and position either by entering the coordinates or by drag-and-dropping the element and element’s sides in the designer.
- Kind – Set how the selected element is displayed in the view.
- Text: Show text as is.
- Image: When you select a field for which the Kind is changed to Image, the field’s value is taken as the image name. So for example, if you set the status code field as Image, and add the icons of the different status codes to the customization, the icon on the view will change according to the record’s status code. Also, please see the Form Style Editor’s Folder description for more information.
- Map Pin: When you select a field for which the Kind is changed to Map Pin, the field’s value is taken as the Map Pin image name. So for example, if you set the status code field as Map Pin, and add the icons of the different status codes to the customization, the Map Pin icon on the map view will change according to the record’s status code. Also, please see the Form Style Editor, ImageCell Folder property description for more information.
- Text-Edit, Text-DirectEdit, Image-Edit, Image-DirectEdit: The element becomes editable directly from the view. See Editable field
- Text-Click, Image-Click: Clicking the element opens details about related entity record. See Clickable field.
- Style – You can select the style that will be used for the selected element. The designer will also preview the selected style. You can also create your own styles or adjust the existing ones using the Edit Styles button in the toolbar.
- Binding – Please check the following section for more information.
- Anchor - Anchors fix the boundary position of the field to the side the anchor is pointing to.
Binding
Binding determines which entity field is displayed in a cell. It is actually a combination of two properties: type and value.
Three binding types exist:
- Value - this is the default option. This way the field data is shown in standard way, so that you can see the value of the field in Mobile CRM app.
- Raw Value - this makes sense for example for option sets, if you want to display the numeric representation of an option, rather than its label. This is useful, if you don’t want to display text, but different view images, or map pins based on different value of the option set. It is because images cannot have space in their names
- Constant - this binding type allows you to enter static text. The exact text is displayed in the app, instead of the entity field data. This way you can add labels to views, for example to describe fields that only show numeric values.
Edit styles
To change existing styles or add new styles, select Edit Styles from the toolbar.
The styles are global for all fields on all views, so if you change a style that is assigned to multiple fields, even to a view on a different entity, these changes are also applied to these fields. It does not matter from which view you open the style editor. Click Dependencies to see all components where a style is used.
These are the properties of an image cell (used when the Kind = Image):
- Folder – Name of the Folder under the platform folder of the Image.zip where the icons for the field values that you want to represent as pictures are stored.
- BackColor
- ForeColor – If the icon that you want to use, is colorized, you can change the color of it here.
- FormatString – If you use a non-string field as a source for the image (e.g. a lookup field), the string should look like folder_name{0}.png. {0} represents the target name (name of the lookup record, according to which the image is used.
- HorizontalAlignment – NEAR aligns the image to the left side of the cell, FAR aligns image to the right side of the cell and CENTER aligns the image to middle of the cell.
- ImageQuery
- Name – Name of the style.
- VerticalAlignment – NEAR aligns the image to the upper side of the cell, FAR aligns the image to the bottom of the cell, CENTER aligns the image to the middle of the cell.
These are the properties of a text cell (used when the Kind = Text):
- AutoHeight – Adjusts the row’s height to fit the field in case the field element in designer is smaller than the font.
- BackColor – Color of the field’s background (color of the cell).
- EllipsisPosition
- FontName, FontSize, FontWeight - Specify the font.
- ForeColor – Color of the foreground element – in this case it's the text (#AARRGGBB – AA = alpha/transparency, RR = red channel, GG = green channel, BB = blue channel).
- FormatString – You can format the way the field data is represented, e.g. you can enter a format string in the way “Personal: {0}” where Personal: is a static text and the field data is entered where the element {0} is.
- HorizontalAlignment – NEAR aligns the text to the left side of the cell, FAR aligns text to the right side of the cell and CENTER aligns the text to middle of the cell.
- Name – Name of the style.
- VerticalAlignment – NEAR aligns the text to the upper side of the cell, FAR aligns the text to the bottom of the cell, CENTER aligns the text to the middle of the cell.
Additional configuration
A view can include additional components, not only entity fields. You can also configure how the data should be displayed.
Buttons
You can add buttons to the view. These are displayed when a record is selected in the list.
Buttons must be enabled:
- Each user can control the behavior in their mobile app, In the app, go to Setup and enable Appearance > List Buttons.
- In the configuration of a project (while edit an app project in Woodford, select Configuration from Project menu and search for button).
- Select Buttons from the toolbar.
- The right pane shows your available commands, the left pane shows commands in use. Add buttons from right to left.
- For some commands you can specify more details, for example what child entity record to create or which status to set for the record.
Edit filter
Edit Filter is used to restrict the displayed data in the view to only those that meet the specified conditions. The difference between Sync Filter and Edit Filter is that the Sync Filter allows the sync only of those fields that meet the conditions, while the Edit Filter works with all fields and only displays those that meet the conditions. This is the perspective of having more views for one entity.
Edit sort
Edit Sort allows you to select which field will be used for sorting and the direction of sorting (ascending or descending).
You can also sort by multiple fields.
Edit search
Click Edit Search to define where (in which field) will the application search for the character entered into the application’s search field. Also, it can be defined whether to search at the field’s beginning, end or in each full text. You can add multiple fields, the conditions are combined using the logical operation OR.
Because the search uses OR, to enable more advanced search, you can create a filter with a condition over a text field (e.g. Name, Title etc.) and enter @@filter@@ as a filtered text. This will be replaced (in runtime) by the text entered into the search field on the view.
If you have fields for GPS coordinates in the entity, and if you enable this option for the mobile project, users will be able to switch the view from list to map; the records will be displayed on the map.
Actions when multiple records are selected
It‘s possible to define actions for Views when MultiSelect is triggered. To trigger it, you need to tap and hold a record in view where at least one MultiSelect button is enabled. Then you can select multiple records and the selected action will be performed on all selected records.
To see how it works, please check this WEBINAR SECTION. Webinar
Add Image, Add Map Pin
Adding images is shown in section 5.3.1 TBD and adding a custom map pin in section 5.3.2 TBD.
You can also watch this WEBINAR for more info on Map Pins. Webinar
Sort fields and filter fields
Since version 9.1 of Mobile CRM app, you can set up additional sorting and filtering on view by using the Search bar. In these two view options, you can specify which fields are available to users for this additional sorting and filtering.
Date fields
Click Date Fields to specify which fields that are used as Start and End date fields. This can be useful if you want to allow Calendar view for this entity.
Multiple views
Advanced view features
Row scripts
You can define multiple row designs for a view, and then you can define conditions when specific row design should be used. In the following example, we will create a second row with red background, this will be used when the field Name does not contain data.
| Note | Please check this BLOG POST for an additional example of row script use. Blog |
Creating a second row
You have multiple options for creating rows:
- Click Clone Row to create a copy of the row selected in the Properties pane. Then rename the row.
- Click Add Row to create an empty row, where you can add fields and design it from scratch.
- You can also click Copy Design to copy the design of any view from any entity.
Creating a new style with red background
- Click Edit Styles to display the styles designer.
- Select primary from the style list, and then click Add. This creates a clone of the primary style.
- Change the BackColor (background), ForeColor (text color), and rename the style (for example Red Primary).
- Click Save & Close to close the styles editor and return to the view designer.
- In the new row, select a cell and change the style from Primary to Red Primary.
Creating a row script
To define when and how the different the row designs are used, you need to set up a row script. Row script is a combination of steps and conditions (what should happen and when).
Click Row Script to open the script editor. Add conditions and steps, then click Save & Close.
| Warning | Please do not use Load reference in Row Script, even when it is possible. It will not work and could cause issues. |
Changing style on view dynamically
Since version 10.1, there is also a different option in changing the field style on View dynamically, based on its value or other conditions instead of creating a different row design. It is also possible to change the field’s style by using Row Script directly.
To learn more about this approach, please check this part of WEBINAR and HERE to see the setup and see it in action. Webinar
Best practice in renaming a view
Keep in mind that the view name is used as a logical name, so it's used all over the application. If someone changes the name of a view, it can cause issues with the application. Especially if they rename default view names on pre-defined entities.
Views are used in map, calendar, in entities as public, associated, or lookup views. So when the name is changed, you should reset the views on all these places.
It might be easier to use Localization feature to change the display name of a view, while keeping the logical name untouched. To enable this, you need to keep the view names without spaces or special characters (underscore is ok).
Editable field
Editable field, list, or editable grid is a feature that allows users to edit more records at once, directly from the view, without a need to go to edit form of a record.
To set a field to be editable directly in the view, set the field's Kind to one of the edit options.
The main difference between Edit and DirectEdit is that changes made on fields with the Edit option, need to be saved. Since the Save button for view changes is available only in the Public view (list of records accessed from Home), DirectEdit option saves changes in field immediately after editing, without the need for user to click Save.
For the use on lookup or associated views, you need to use the DirectEdit option only, otherwise changes on different records will not be saved correctly.
Hint: For more information about editable fields, please check this section of one of our webinars. Webinar
Clickable field
Clickable fields allow you to add a hyperlink of a lookup field to a view. When you tap the field, details of the lookup target record open. This can serve as a kind of a shortcut / quick access; for example to the parent account from an opportunity view.
To enable a clickable field on a view, set the field’s Kind to Text-Click or Image-Click.
Inline frames
It’s possible to add JavaScript and JSBridge to views and perform validation, when you use the view to change the data (editable fields, MultiSelect) and to handle view buttons. It is also possible to use JavaScript and JSBridge to load records to the view (FetchXML).
For more information about extending views by using this technology, please check the following part of a webinar. Webinar
There are additional validation options, like the possibility for the app to ask whether a change should be saved or discarded, when users edit records on lists;
OnChange and OnSave actions triggering in JavaScript, validations when records are modified or saved directly on a list, etc. can be seen in this webinar. Webinar
Search view
It is possible to create a specific view used to display search results. This needs to be a public view named SearchView and it cannot be hidden. You can set up different looks and functionality of this view.
To see it in action, please check this WEBINAR SECTION]. Webinar
Responsive view / list
In order to use larger screens on tablets (or phones with large screens) to their full potential, it is possible to adjust the view design to be more responsive, i.e., to use the screen more effectively.
To learn how it can be achieved, please check the following blog post. Blog
Automatic list / view headers
It is possible to add headers, field names on the list. To learn more, please check this part of a webinar. Webinar
This feature does not require setup in Woodford project. It allows to see some additional information when using multiselect in Resco Mobile CRM app, like number of selected items vs number of all items in the view or setting up the aggregation (e.g. sum of total amount on Opportunity) for selected vs all items in the view.
To learn more, please check this part of a webinar and this part to see it in action. Webinar