View: Difference between revisions
| (91 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Views are one of the main components of mobile apps. The main purpose of a view is to display a list of records of a particular [[entity]]. | Views are one of the main components of mobile apps. The main purpose of a view is to display a list of records of a particular [[entity]]. | ||
Views | Views are defined within [[app projects]]. Each entity has its own views. A single entity can have multiple views. | ||
* Administrators can create and manage views in [[Woodford]]. | |||
* App users can create their own custom views directly in the app. See [[Private view]]s. | |||
== Types of views == | == Types of views == | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
{{Note|If a custom associated view, lookup view, or dashboard view does not exist, the public view is used instead.}} | {{Note|If a custom associated view, lookup view, or dashboard view does not exist, the public view is used instead.}} | ||
Views display a single entity. If you want to display a hierarchy of records from multiple entities linked by a parent-child relationship, try the '''[[tree view]]'''. | |||
== Managing views == | == Managing views == | ||
Views are associated with an entity. To see a list of views for an entity, edit an app project, select the entity and click '''Show UI'''. | Views are associated with an entity. To see a list of views for an entity, edit an app project in Woodford, select the entity and click '''Show UI'''. | ||
On the '''Mobile Views, Forms and Charts''' screen, you can add, clone, or remove views, edit them and change their properties, as well as export them (to a file in XML format) or import them (for example, to a different app project). | On the '''Mobile Views, Forms and Charts''' screen, you can add, clone, or remove views, edit them and change their properties, as well as export them (to a file in XML format) or import them (for example, to a different app project). | ||
| Line 26: | Line 30: | ||
You can define multiple views for each entity. While you can select an initial default view in the properties of a view, users can switch to a different view in the app. Users may not switch to hidden views; those are displayed only when explicitly configured. | You can define multiple views for each entity. While you can select an initial default view in the properties of a view, users can switch to a different view in the app. Users may not switch to hidden views; those are displayed only when explicitly configured. | ||
[[File:List-of-view-forms-charts.png|600px|alt=List of mobile views, forms, and charts for the Task entity.]] | |||
== Creating a view == | |||
# Select an entity in the '''Project''' menu; for example, ''Competitor''. | |||
* | # Click '''Show UI''' to display the list of mobile views, forms, and charts. | ||
# Click '''New View''' and set the properties of the view. | |||
# Enter a descriptive '''Name'''; for example ''Competitors''. | |||
#: The name of a view is used as a logical name. Read also the [[View#Best_practice_in_renaming_a_view|best practices]] and [[Localization_examples#Rename_views|instructions for renaming views using localization]]. | |||
# As '''Type''', select one of the four view types: | |||
#* '''Public List''' displays the list of records of an entity. Usually what you see after opening an entity in application from Home screen. It can be used everywhere | |||
#* '''Associated List''' displays a list of records from an associated entity, that is relevant for the selected item. Example: A list of appointments of a particular contact. | |||
#* '''Lookup List''' displays the list of records of an entity (same as public view), however, it is used when the user should select a record. | |||
#* '''Dashboard List''' is designed for use in a [[Dashboard]]. | |||
# As '''Template''', select one of the provided templates or use a blank one to start from scratch. | |||
#:Keep in mind the limited screen size of a mobile device. We recommend to use templates; adapting is often less work than creating a template. | |||
# Select '''Hidden''' if you don't want that your new view is listed as an option in the app to users when they switch views. However, the view can still be used in the app when you explicitly design it that way. | |||
# Click '''OK''' to start designing your view. | |||
== Properties of an existing view == | |||
When you edit the properties of an existing view (select the view and click '''Properties'''), you can no longer change the template (that's only the starting design of a view), but configure additional parameters: | |||
* '''Default''' – Make this view the default initial view. If the default is not set, the first view in alphabetical order is used. | |||
* | : The default selection only applies when a user synchronizes with an app project for the first time. The app remembers the user's choice and does not override it, even if a Woodford admin later decided to set up a different view as the initial default. | ||
* '''Mode''' – Make this view dedicated for online or offline view, or for both. | |||
* | * '''Sync Filter''' – Select if you want to use [[Sync Filter]] also in online mode for this view. | ||
== View designer == | |||
The view designer window is divided into multiple parts: | |||
* '''Toolbar''' with buttons on top: Use it to add or remove elements from your view or configure additional functions. | |||
* '''Properties''' pane on the left shows the properties of the selected component in the '''Editor''' pane. | |||
* '''Editor''' pane in the center shows your row design(s). | |||
* '''Fields''' pane on the right shows fields you can add to the view. | |||
[[File: | [[File:View-designer-main-screen.png|600px|alt=View designer in Woodford: main screen]] | ||
=== Fields pane === | |||
The '''Fields''' pane lists all the fields and variables available in the view. | |||
* Use the + button to manage the fields. When displaying the view, Resco mobile apps fetch all the listed fields from the database. Keeping the list short can speed up the performance. | |||
* Drag fields from the Fields pane to the Editor pane to add them to your row design. | |||
* Not all fields must be displayed - the additional fields can be used for sorting and filtering. | |||
[[File:Select-fields-in-view.png|600px|alt=select fields in view]] | |||
If a field is not listed in the Select Fields window, it is probably not enabled for the app project. See [[Data_model_in_mobile_apps#Managing_fields|Managing fields]] for more information. | |||
=== Editor pane === | |||
The editor pane displays a mockup of the view's row design(s). Each view can contain one or more row designs. See [[Responsive view design]] to learn how multiple rows can be beneficial for your app. | |||
Use the editor pane to arrange and resize fields in the view. | |||
* Select any component of the view to display its properties. | |||
* Drag fields from the Fields pane to add them to your view. | |||
* To change the content of a cell, select it and change the Value property. (Or double-click the plus symbol next to a field on the Fields pane.) | |||
=== Properties pane === | |||
The following properties can be configured on '''View''' level: | The following properties can be configured on '''View''' level: | ||
* Default layout: Use list to display one record per line. Use grid to allow multiple records per line. This can be particularly useful for wider displays and/or if you want to create your view as a gallery of images. | |||
* Auto table: Enable this option if you want to switch to an Excel-like table view. Table view is used when the available screen width exceeds a threshold value ('''Breakpoint'''). You '''can''' modify the style of the entries; see [[Style_editor#Tricks|Tricks]]. | |||
* | |||
* Show header: When enabled, it creates a header row above the data rows. See [[View#Header|Header]] for more information. | |||
* | The following properties can be configured on '''Row''' level. Select the row in the '''Editor''' pane to display its properties. | ||
* Name – Defines the Row’s name (to distinguish between multiple Row designs). | |||
* Dimension – Defines the width and height of the row in a view. | |||
* Color (Background) – Defines the color of the row’s background. | |||
* Color (Selected) – Defines the color of the row’s background when the record is selected. | |||
* {{Anchor|Next}} Next row – used for custom responsive layout. Define multiple rows of various widths and chain them with this setting. In the app, row design changes as the screen width changes. See [[Responsive view design]] for more information. | |||
The following properties can be configured on '''Cell''' level. Select the cell in the '''Editor''' pane to display its properties. | |||
* Cell – Shows the selected cell. | |||
* Kind – Set how the selected element is displayed in the view. | * Kind – Set how the selected element is displayed in the view. | ||
** Text: Show text as is. | ** Text: Show text as is. | ||
** Image: When you select a field for which the Kind is changed to Image, the field’s value is taken as the image name. So for example, if you set the status code field as Image, and add the icons of the different status codes to the customization, the icon on the view will change according to the record’s status code. Also, please see the Form Style Editor’s Folder description for more information. | ** Image: When you select a field for which the Kind is changed to Image, the field’s value is taken as the image name. So for example, if you set the status code field as Image, and add the icons of the different status codes to the customization, the icon on the view will change according to the record’s status code. Also, please see the Form Style Editor’s Folder description for more information. | ||
** Map Pin: When you select a field for which the Kind is changed to Map Pin, the field’s value is taken as the Map Pin image name. So for example, if you set the status code field as Map Pin, and add the icons of the different status codes to the customization, the Map Pin icon on the map view will change according to the record’s status code. | ** Map Pin: When you select a field for which the Kind is changed to Map Pin, the field’s value is taken as the Map Pin image name. So for example, if you set the status code field as Map Pin, and add the icons of the different status codes to the customization, the Map Pin icon on the map view will change according to the record’s status code. See [[custom map pins]] for more information. | ||
** Text-Edit, Text-DirectEdit, Image-Edit, Image-DirectEdit: The element becomes editable directly from the view. See [[#Editable_field|Editable field]] | ** Text-Edit, Text-DirectEdit, Image-Edit, Image-DirectEdit: The element becomes editable directly from the view. See [[#Editable_field|Editable field]]. | ||
** Text-Click, Image-Click: Clicking the element opens details about related entity record. See [[#Clickable_field|Clickable field]]. | ** Text-Click, Image-Click: Clicking the element opens details about related entity record. See [[#Clickable_field|Clickable field]]. | ||
* Style – You can select the style that will be used for the selected element. The designer will also preview the selected style. You can also create your own styles or adjust the existing ones using the '''Edit Styles''' button in the toolbar. | * Binding (Type, Value) – See the next section for more information. | ||
* | |||
* Layout (X, Y, W, H) – Coordinates of the top left corner of the cell, and cell's width and height. You can adjust cell size and position either by typing the coordinates or by dragging the cell or its sides in the editor. | |||
* Style – You can select the style that will be used for the selected element. The designer will also preview the selected style. You can also create your own styles or adjust the existing ones using the '''[[Style editor|Edit Styles]]''' button in the toolbar. | |||
* Responsive – Specify if the cell should grow/shrink to fit row width change or remain constant. In the case of images, disable responsive resizing. See [[Responsive_view_design#Responsive_fields|responsive fields]] for details. | |||
=== Binding === | ==== Binding ==== | ||
Binding determines which entity field is displayed in a cell. It is actually a combination of two properties: type and value. | Binding determines which entity field is displayed in a cell. It is actually a combination of two properties: type and value. | ||
Three binding types exist: | Three binding types exist: | ||
* Value | * Value – this is the default option. This way, the field data is shown in a standard way so that you can see the value of the field in the Mobile CRM app. | ||
* Raw Value | * Raw Value – this makes sense, for example, for option sets, if you want to display the numeric representation of an option, rather than its label. This is useful if you don’t want to display text but different view images or map pins based on different values of the option set. It is because images cannot have space in their names. | ||
* Constant | * Constant – this binding type allows you to enter static text. The exact text is displayed in the app instead of the entity field data. This way you can add labels to views, for example, to describe fields that only show numeric values. | ||
== Toolbar functions == | |||
[[File:View toolbar cell section.png|alt=View toolbar, Cell section]] | |||
The toolbar is divided into related blocks. The first section, ''Cell'', contains functions for managing cells in your view. | |||
* Cell Up, Cell Down - Use these buttons to modify the order of the cells in a view. In Woodford, you can see the order on the '''Properties''' pane in the '''Cell''' parameter. In the app, cells are displayed in the same order. This only comes into play if you design overlapping cells with a solid background. For example, if you want to use a background image for your view, create an image cell that covers the entire view and move it to the first position (so it is displayed first). | |||
* Add Cell – Add a new text cell to the view. | |||
* Delete Cell – Remove the select cell from the view. | |||
=== Images and map pins === | |||
Click '''Add Image''' and select the type of image to add an image to your view. See [[Images#Add_images_to_views_and_forms|Add images to views and forms]] for more information. | |||
Click '''Add Map Pin''' to add a map pin image to your view. You can then select many options for the map pins or use custom pins. See [[Custom map pins]] for more information. | |||
You can also watch this [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9o9MS6gldr4 WEBINAR] for more info on Map Pins. {{Badge|Webinar}} | |||
=== Edit styles === | |||
To change existing styles or add new styles, select '''Edit Styles''' from the toolbar. | |||
The styles are global for all fields on all views, so if you change a style assigned to multiple fields, even to a view on a different entity, these changes are also applied to these fields. It does not matter from which view you open the style editor. Click '''Dependencies''' to see all components where a style is used. | |||
See '''[[Style_editor#Views_and_home_screen|Style editor]]''' for more information. | |||
=== Buttons === | === Buttons === | ||
You can add buttons to the view. Depending on your device, buttons are displayed when you select a record in the list, or when you swipe from the right. | You can add buttons to the view. Depending on your device, buttons are displayed when you select a record in the list, or when you swipe from the right. | ||
Buttons | [[File:Buttons.png|600px|alt=View buttons in Resco mobile apps]] | ||
On Windows apps, buttons are displayed when you select a record. On Android and iOS, the behavior is controlled by the parameter '''Use Legacy List Buttons''' (in Woodford '''[[Configuration]]'''). | |||
<!-- Each user can control the behavior in their mobile app, In the app, go to '''[[Setup]]''' and enable '''Appearance > List Buttons'''. (not possible since release 13)--> | |||
To add buttons to the view, proceed as follows: | To add buttons to the view, proceed as follows: | ||
# Select '''Buttons''' from the toolbar to display the [[command editor]]. | |||
# The right pane shows your available commands, the left pane shows commands in use. Add buttons from right to left. | |||
# For some commands you can specify more details, for example, what child entity record to create or which status to set for the record. Select the command and click '''Properties'''. | |||
# Save all changes and publish the project. | |||
{{Note|To use buttons like E-mail or Call, the email address or telephone number fields must be included in the view. Also, [[Data_model_in_mobile_apps#formatting|Formatting]] of the field has to set correctly.}} | |||
You can also define custom buttons: | |||
# Select '''Buttons''' from the toolbar. | # Select '''Buttons''' from the toolbar. | ||
# | # Click '''New Command''' and enter an internal name of the command and a label, then click '''OK'''. | ||
# | # Save the buttons editor and return to the view. | ||
# Select '''Button Click''' from the toolbar. | |||
# Using the [[rules editor]], define an action that the button should perform. | |||
=== Actions when multiple records are selected === | === Actions when multiple records are selected === | ||
Similar to buttons, you can define actions available when you select multiple records in your view. | Similar to buttons, you can define actions that are available when you select multiple records in your view. To use multi-selection in the app, tap and hold a record until the selection checkboxes appear, or use the [[Releases/Winter_2025#Multiselect_records_on_maps|lasso tool on map views]]. Multi-selection offers the following functions: | ||
* Access configurable commands from the hamburger menu in the top right corner. For example, you can export the selected records, or delete them. | |||
* Tap '''Sum''' in the bottom right corner to access statistics/aggregation functions. | |||
* Tap '''Items''' in the bottom left corner to "select all" or "select none". | |||
[[File:Multiselect-records-commands-aggregates.mp4|600px|alt=Selecting multiple records in views in Resco mobile apps]] | |||
In Woodford, edit a view and click '''Multi Select''' to set up the available commands. The operation is similar to view buttons or [[Command_editor#View_commands|Form commands]]. To see how it works, you can also check this [https://youtu.be/REgaV6ymYWM?t=20m27s webinar section]. {{Badge|Webinar}} | |||
You can define your own [[Command_editor#Custom_commands|custom commands]] that perform actions that are not available when using built-in commands. The actions cannot be configured in Woodford, you can define them using [[Resco JavaScript Bridge|JavaScript]]. See the [https://www.resco.net/javascript-bridge-reference/#MobileCRM_UI_EntityList_onCommand MobileCRM.UI.EntityList.onCommand] function for more information. | |||
You can disable multi-selection in views completely using [[Configuration#List|Woodford configuration]]: '''Allow Multi-select In Lists'''. | |||
=== Import design === | |||
If you are creating custom view designs for your entities and you want to ensure that the design is consistent across the entire project, you can use the '''Import Design''' function. Select the entity, view, and row design that you want to use. You can either select one of your custom designs or a built-in design. You can also choose which parts of the view should be imported. | |||
[[File:Import-design-in-views.png|600px|alt=import design in views]] | |||
== Sorting and filtering == | |||
[[File:View toolbar query section.png|alt=View toolbar, Query section (sorting and filtering)]] | |||
=== Select fields === | |||
Click '''Select Fields''' to define which fields for the main entity, or even from related entities, should be available in the view. These fields are loaded from the database when the view is displayed. All fields that are displayed in the view must be loaded, but you can also load additional fields, for example, if you want to allow the user to filter the view according to these fields. | |||
=== Edit filter === | === Edit filter === | ||
'''Edit Filter''' is used to restrict the displayed data in the view to only those that meet the specified conditions. The difference between [[Sync Filter]] and | '''Edit Filter''' is used to restrict the displayed data in the view to only those that meet the specified conditions. Conditions are defined using the generic [[Filter editor]] user interface. | ||
The difference between [[Sync Filter]]s and view filters is that the Sync Filter controls which records from the backend make it to the offline database on the device, while the view filter determines which of the records available on the device are displayed in a particular view. This is the perspective of having more views for one entity. | |||
=== Edit sort === | === Edit sort === | ||
| Line 145: | Line 220: | ||
=== Edit search === | === Edit search === | ||
Click '''Edit Search''' to define where (in which field) will the application search for the character entered into the application’s search field. Also, it can be defined whether to search at the field’s beginning, end or in each full text. You can add multiple fields, the conditions are combined using the logical operation OR. | Click '''Edit Search''' to define where (in which field) will the application search for the character entered into the application’s search field. Also, it can be defined whether to search at the field’s beginning, end, or in each full text. You can add multiple fields, the conditions are combined using the logical operation OR. | ||
Because the search uses OR, to enable more advanced search, you can create a filter with a condition over a text field (e.g. Name, Title etc.) and enter @@filter@@ as a filtered text. This will be replaced (in runtime) by the text entered into the search field on the view; see [[Filter_editor#Using_search_strings_in_filters|example]]. | |||
Searching is generally fast, however, these are some of the factors that affect search speed: | |||
* number of records in an entity where you search | |||
* view filters with linked entities | |||
* complexity of the database | |||
* device performance (power) | |||
* number of fields used in search | |||
If you have fields for GPS coordinates in the entity, and if you enable this option for the mobile project, users will be able to switch the view from list to map; the records will be displayed on the map. | If you have fields for GPS coordinates in the entity, and if you enable this option for the mobile project, users will be able to switch the view from list to map; the records will be displayed on the map. | ||
=== Sort fields and filter fields === | === Sort fields and filter fields === | ||
Since version 9.1 of Mobile CRM app, you can set up additional sorting and filtering on view by using the Search bar. In these two view options, you can specify which fields are available to users for this additional sorting and filtering. | Since version 9.1 of Mobile CRM app, you can set up additional sorting and filtering on view by using the Search bar. In these two view options, you can specify which fields are available to users for this additional sorting and filtering. | ||
=== | === Calendar fields === | ||
Click ''' | Click '''Calendar Fields''' to customize how this view behaves on the [[Calendar]]. | ||
* On the '''Dates''' tab, specify which fields are used as Start and End date fields. | |||
* On the '''Cards''' tab, configure which details appear on the task card in Day or Week view. By default, only Header is shown, but you can add up to two more fields (maximum three). | |||
== | == Business logic == | ||
Resco mobile apps support custom [[business logic]] for adding advanced features to your views. Views support the following actions that trigger no-code scripts (rules). Rules are edited in the [[Rules_editor]]. | |||
* [[Row Script]] – executed for each row when a view is loading or refreshing | |||
* [[On Save]] – triggered by saving an [[#Editable_field|Editable field]] | |||
* [[On Change]] – triggered by changing an [[#Editable_field|Editable field]] | |||
* [[Button Click]] – triggered by tapping a view button | |||
* [[Cell Click]] – triggered by tapping a cell | |||
=== Iframes === | |||
You can use [[Offline HTML]] functionality to add JavaScript and JSBridge to views and perform validation; for example when you use the view to change the data (editable fields, MultiSelect), and to handle view buttons. It is also possible to use JavaScript and JSBridge to load records to the view ([[FetchXML]]). For more information about extending views by using this technology, please check the following part of a [https://youtu.be/uocH_yaytq0?t=35m33s webinar]. {{Badge|Webinar}} | |||
There are additional validation options, like the possibility for the app to ask whether a change should be saved or discarded when users edit records on lists; OnChange and OnSave actions triggering in JavaScript, validations when records are modified or saved directly on a list, etc. can be seen in this [https://youtu.be/B5mMIqJYy-Y?t=48m15s webinar]. {{Badge|Webinar}} | |||
# | See [[Resco_JavaScript_Bridge#EntityList|Resco JavaScript Bridge]] for more information. | ||
{{Note|If you are using JavaScript to provide source data for a view, this applies to the default list view, but not to the map view. Map views and [[route plan]]s use the original fetch in the view combined with the latitude and longitude of the area currently displayed on the map; custom data provided by JSBridge are ignored.}} | |||
== Miscellaneous == | |||
=== Flipping between list, map, and chart === | |||
The traditional way of displaying records is as a list. If the records include location information, users can flip the view to a map. If the entity has a chart defined, users can flip to that as well. | |||
[[File:Flipping-between-view-map-chart.mp4|600px|alt=flipping between view map chart]] | |||
=== Map view === | |||
Records can be displayed on a map if they include geographic coordinates, i.e., latitude and longitude fields. Woodford comes with the '''[[Geocoding]]''' feature that can convert street addresses into latitude and longitude. | |||
If you don't like the standard map pins, you can configure '''[[custom map pins]]''', including the option to use different pins for different record types. If there are too many pins to fit into the map, you can [[Custom_map_pins#More_options|enable map pin aggregation]]. | |||
Users can tap any pin to display details about the record. Or they can use the lasso tool to select multiple records and perform bulk actions. Standard '''[[View#Actions_when_multiple_records_are_selected|multi-select]] commands''' can be used directly from the map. | |||
[[File:Multi-select-records-on-the-map.png|600px|alt=select multiple records using the lasso tool]] | |||
=== Best practice in renaming a view === | === Best practice in renaming a view === | ||
Keep in mind that the view name is used as a logical name, so it's used all over the application. If someone changes the name of a view, it can cause issues with the application. Especially if they | Keep in mind that the view name is used as a logical name, so it's used all over the application. If someone changes the name of a view, it can cause issues with the application. Especially if they change the default view names on pre-defined entities. | ||
Views are used in map, calendar, in entities as public, associated, or lookup views. So when the name is changed, you should reset the views on all these places. | Views are used in map, calendar, in entities as public, associated, or lookup views. So when the name is changed, you should reset the views on all these places. | ||
It might be easier to use [[Localization]] feature to change the display name of a view, while keeping the logical name untouched. To enable this, you need to keep the view names without spaces or special characters | It might be easier to use [[Localization]] feature to change the display name of a view, while keeping the logical name untouched. To enable this, you need to keep the view names without spaces or special characters. Underscore is okay to use, but the following characters are not: <code><nowiki>/\%#&*<>?|“+:{}</nowiki></code>. Also, some national characters and non-Latin characters are not allowed. See [[Localization examples]] for inspiration. | ||
=== Editable field === | === Editable field === | ||
| Line 226: | Line 295: | ||
* '''DirectEdit''': Changes are changed immediately. This can be used also on lookup or associated views that don't have the Save button. | * '''DirectEdit''': Changes are changed immediately. This can be used also on lookup or associated views that don't have the Save button. | ||
For more information about editable fields, please check this section of one of our [https://youtu.be/pYbmWlqLFh8?t=20m18s webinars]. {{Badge|Webinar}} | For more information about editable fields, please check this section of one of our [https://youtu.be/pYbmWlqLFh8?t=20m18s webinars]. {{Badge|Webinar}} The webinar is dated, but much of the information is still valid. One notable correction: editable views fully support validation using rules. | ||
;Text-Edit versus Image-Edit | |||
:Text-Edit and Text-DirectEdit can be used by cells with binding to any field that allows input, such as Text, Number, OptionSet, etc. | |||
:Image-Edit and Image-DirectEdit can only be used on Image cells with binding to OptionSet field. In this case, the app lets users choose from a list of options. This is especially useful when you use images representing the status of a record. For example, you can represent the status of work orders by icon and let users change it by tapping the icon. Detailed example: [[Image_examples#Display_"two_options"_as_checkbox_on_a_view|Display "two options" as a checkbox on a view]]. | |||
=== Clickable field === | === Clickable field === | ||
| Line 234: | Line 307: | ||
To enable a clickable field on a view, set the field’s '''Kind''' to Text-Click or Image-Click. | To enable a clickable field on a view, set the field’s '''Kind''' to Text-Click or Image-Click. | ||
=== | === Header === | ||
Enable '''Auto Header''' in the [[View#Properties_pane|view properties]] to create a header row above the data rows. The header row allows simple sorting. This parameter affects your current view, but you can also configure the project-wide setting in [[Configuration#List|Configuration]], find '''Auto List Header''' under '''UI > List'''. To learn more, please check this part of a [https://youtu.be/B5mMIqJYy-Y?t=4m45s webinar]. {{Badge|Webinar}} | |||
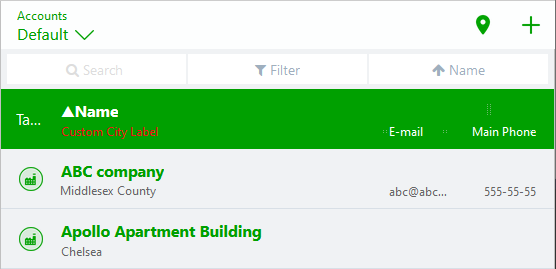
[[File:Custom label in view headers.png|alt=custom label in view headers]] | |||
If you need to include a custom label for one of the fields in the header, just like the city in the screen shot, you can use styles: | |||
# Edit the view. | |||
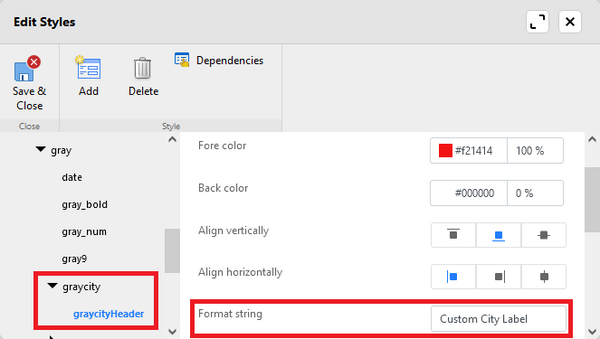
# Create a new style, for example "graycity", and assign it to the City field. | |||
# Create a second style with the same name as above with the suffix "Header", i.e., "graycityHeader". | |||
# Enter the custom label as '''Format string'''. | |||
[[File:Format string for custom view header label.png|600px|alt=Format string for custom view header label]] | |||
Tips: | |||
* In project [[Configuration#List|Configuration]], this corresponds to the setting "Auto List Header". | |||
* If you are using the associated list on a form, make sure to enable vertical scrolling (in the [[Form#Properties_pane|form property "Arrange items"]]). Horizontal scrolling disables headers. | |||
=== List / view footer === | |||
This feature does not require setup in Woodford project. It allows to see some additional information when using multiselect in Resco Mobile CRM app, like number of selected items vs number of all items in the view or setting up the aggregation (e.g. sum of total amount on Opportunity) for selected vs all items in the view. | |||
To learn more, please check this part of a [https://youtu.be/iLZ43KxGEW0?t=14m56s webinar] and this [https://youtu.be/iLZ43KxGEW0?t=19m59s part] to see it in action. {{Badge|Webinar}} | |||
=== Display multiple records in one row === | |||
Traditionally, lists show one record per line. However, you can switch the '''Default layout''' [[#Properties pane|property]] to "as Grid" if you want to display records in multiple columns. | |||
== Special views == | |||
Woodford offers two ''special'' views, one for searching, other for filtering. The following applies to special views. | |||
* To create them, use the '''Special View''' button, not '''New View'''. | |||
* Do not rename them; use the default names (SearchView and FilterView). | |||
* Only one instance of each special view can exist for an entity. | |||
=== Search view === | === Search view === | ||
It is possible to create a specific view used to display search results. This needs to be a public view named SearchView | It is possible to create a specific view used to display search results. The app automatically switches to this view when you are using the search box. | ||
This needs to be a public view named exactly SearchView; it cannot be hidden. You can set up different looks and functionality of this view. To see it in action, please check this [https://youtu.be/9vL4QRN_1dk?t=31m2s WEBINAR SECTION]. {{Badge|Webinar}} | |||
=== Filter view === | |||
Filter view is used when using an inline filter in a lookup form. | |||
== Private views == | |||
App users can create and manage their own custom views. See [[Private view]] for more information. | |||
{{Feedback}} | |||
[[Category:Woodford]] | [[Category:Woodford]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:49, 14 January 2026
Views are one of the main components of mobile apps. The main purpose of a view is to display a list of records of a particular entity.
Views are defined within app projects. Each entity has its own views. A single entity can have multiple views.
- Administrators can create and manage views in Woodford.
- App users can create their own custom views directly in the app. See Private views.
Types of views
- Public view displays the list of records of an entity.
- Example: A list of your contacts.
- Associated view displays a list of records from an associated entity, that is relevant for the selected item.
- Example: A list of appointments of a particular contact.
- Lookup view displays the list of records of an entity (same as public view), however, it is used when user should select an entity to be inserted into a form.
- Dashboard view is a combination of multiple views and charts.
| Note | If a custom associated view, lookup view, or dashboard view does not exist, the public view is used instead. |
Views display a single entity. If you want to display a hierarchy of records from multiple entities linked by a parent-child relationship, try the tree view.
Managing views
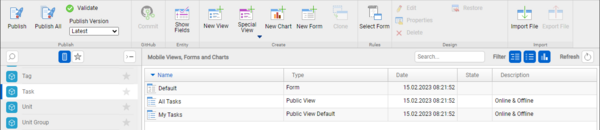
Views are associated with an entity. To see a list of views for an entity, edit an app project in Woodford, select the entity and click Show UI.
On the Mobile Views, Forms and Charts screen, you can add, clone, or remove views, edit them and change their properties, as well as export them (to a file in XML format) or import them (for example, to a different app project).
You can define multiple views for each entity. While you can select an initial default view in the properties of a view, users can switch to a different view in the app. Users may not switch to hidden views; those are displayed only when explicitly configured.
Creating a view
- Select an entity in the Project menu; for example, Competitor.
- Click Show UI to display the list of mobile views, forms, and charts.
- Click New View and set the properties of the view.
- Enter a descriptive Name; for example Competitors.
- The name of a view is used as a logical name. Read also the best practices and instructions for renaming views using localization.
- As Type, select one of the four view types:
- Public List displays the list of records of an entity. Usually what you see after opening an entity in application from Home screen. It can be used everywhere
- Associated List displays a list of records from an associated entity, that is relevant for the selected item. Example: A list of appointments of a particular contact.
- Lookup List displays the list of records of an entity (same as public view), however, it is used when the user should select a record.
- Dashboard List is designed for use in a Dashboard.
- As Template, select one of the provided templates or use a blank one to start from scratch.
- Keep in mind the limited screen size of a mobile device. We recommend to use templates; adapting is often less work than creating a template.
- Select Hidden if you don't want that your new view is listed as an option in the app to users when they switch views. However, the view can still be used in the app when you explicitly design it that way.
- Click OK to start designing your view.
Properties of an existing view
When you edit the properties of an existing view (select the view and click Properties), you can no longer change the template (that's only the starting design of a view), but configure additional parameters:
- Default – Make this view the default initial view. If the default is not set, the first view in alphabetical order is used.
- The default selection only applies when a user synchronizes with an app project for the first time. The app remembers the user's choice and does not override it, even if a Woodford admin later decided to set up a different view as the initial default.
- Mode – Make this view dedicated for online or offline view, or for both.
- Sync Filter – Select if you want to use Sync Filter also in online mode for this view.
View designer
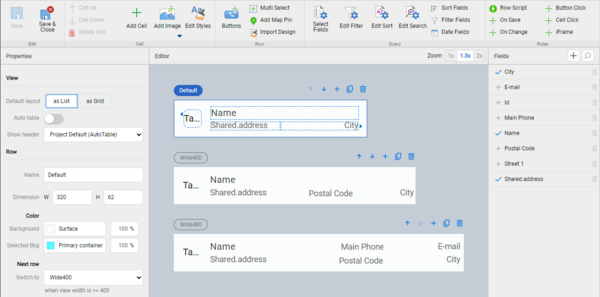
The view designer window is divided into multiple parts:
- Toolbar with buttons on top: Use it to add or remove elements from your view or configure additional functions.
- Properties pane on the left shows the properties of the selected component in the Editor pane.
- Editor pane in the center shows your row design(s).
- Fields pane on the right shows fields you can add to the view.
Fields pane
The Fields pane lists all the fields and variables available in the view.
- Use the + button to manage the fields. When displaying the view, Resco mobile apps fetch all the listed fields from the database. Keeping the list short can speed up the performance.
- Drag fields from the Fields pane to the Editor pane to add them to your row design.
- Not all fields must be displayed - the additional fields can be used for sorting and filtering.
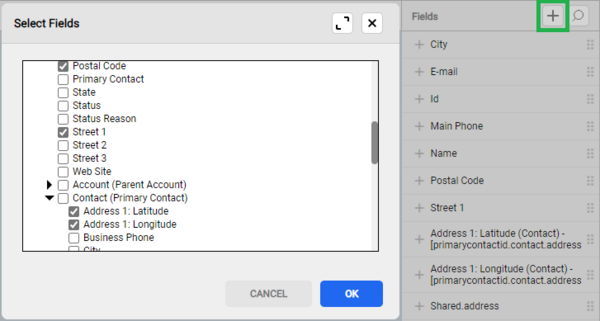
If a field is not listed in the Select Fields window, it is probably not enabled for the app project. See Managing fields for more information.
Editor pane
The editor pane displays a mockup of the view's row design(s). Each view can contain one or more row designs. See Responsive view design to learn how multiple rows can be beneficial for your app.
Use the editor pane to arrange and resize fields in the view.
- Select any component of the view to display its properties.
- Drag fields from the Fields pane to add them to your view.
- To change the content of a cell, select it and change the Value property. (Or double-click the plus symbol next to a field on the Fields pane.)
Properties pane
The following properties can be configured on View level:
- Default layout: Use list to display one record per line. Use grid to allow multiple records per line. This can be particularly useful for wider displays and/or if you want to create your view as a gallery of images.
- Auto table: Enable this option if you want to switch to an Excel-like table view. Table view is used when the available screen width exceeds a threshold value (Breakpoint). You can modify the style of the entries; see Tricks.
- Show header: When enabled, it creates a header row above the data rows. See Header for more information.
The following properties can be configured on Row level. Select the row in the Editor pane to display its properties.
- Name – Defines the Row’s name (to distinguish between multiple Row designs).
- Dimension – Defines the width and height of the row in a view.
- Color (Background) – Defines the color of the row’s background.
- Color (Selected) – Defines the color of the row’s background when the record is selected.
- Next row – used for custom responsive layout. Define multiple rows of various widths and chain them with this setting. In the app, row design changes as the screen width changes. See Responsive view design for more information.
The following properties can be configured on Cell level. Select the cell in the Editor pane to display its properties.
- Cell – Shows the selected cell.
- Kind – Set how the selected element is displayed in the view.
- Text: Show text as is.
- Image: When you select a field for which the Kind is changed to Image, the field’s value is taken as the image name. So for example, if you set the status code field as Image, and add the icons of the different status codes to the customization, the icon on the view will change according to the record’s status code. Also, please see the Form Style Editor’s Folder description for more information.
- Map Pin: When you select a field for which the Kind is changed to Map Pin, the field’s value is taken as the Map Pin image name. So for example, if you set the status code field as Map Pin, and add the icons of the different status codes to the customization, the Map Pin icon on the map view will change according to the record’s status code. See custom map pins for more information.
- Text-Edit, Text-DirectEdit, Image-Edit, Image-DirectEdit: The element becomes editable directly from the view. See Editable field.
- Text-Click, Image-Click: Clicking the element opens details about related entity record. See Clickable field.
- Binding (Type, Value) – See the next section for more information.
- Layout (X, Y, W, H) – Coordinates of the top left corner of the cell, and cell's width and height. You can adjust cell size and position either by typing the coordinates or by dragging the cell or its sides in the editor.
- Style – You can select the style that will be used for the selected element. The designer will also preview the selected style. You can also create your own styles or adjust the existing ones using the Edit Styles button in the toolbar.
- Responsive – Specify if the cell should grow/shrink to fit row width change or remain constant. In the case of images, disable responsive resizing. See responsive fields for details.
Binding
Binding determines which entity field is displayed in a cell. It is actually a combination of two properties: type and value.
Three binding types exist:
- Value – this is the default option. This way, the field data is shown in a standard way so that you can see the value of the field in the Mobile CRM app.
- Raw Value – this makes sense, for example, for option sets, if you want to display the numeric representation of an option, rather than its label. This is useful if you don’t want to display text but different view images or map pins based on different values of the option set. It is because images cannot have space in their names.
- Constant – this binding type allows you to enter static text. The exact text is displayed in the app instead of the entity field data. This way you can add labels to views, for example, to describe fields that only show numeric values.
Toolbar functions
The toolbar is divided into related blocks. The first section, Cell, contains functions for managing cells in your view.
- Cell Up, Cell Down - Use these buttons to modify the order of the cells in a view. In Woodford, you can see the order on the Properties pane in the Cell parameter. In the app, cells are displayed in the same order. This only comes into play if you design overlapping cells with a solid background. For example, if you want to use a background image for your view, create an image cell that covers the entire view and move it to the first position (so it is displayed first).
- Add Cell – Add a new text cell to the view.
- Delete Cell – Remove the select cell from the view.
Images and map pins
Click Add Image and select the type of image to add an image to your view. See Add images to views and forms for more information.
Click Add Map Pin to add a map pin image to your view. You can then select many options for the map pins or use custom pins. See Custom map pins for more information.
You can also watch this WEBINAR for more info on Map Pins. Webinar
Edit styles
To change existing styles or add new styles, select Edit Styles from the toolbar.
The styles are global for all fields on all views, so if you change a style assigned to multiple fields, even to a view on a different entity, these changes are also applied to these fields. It does not matter from which view you open the style editor. Click Dependencies to see all components where a style is used.
See Style editor for more information.
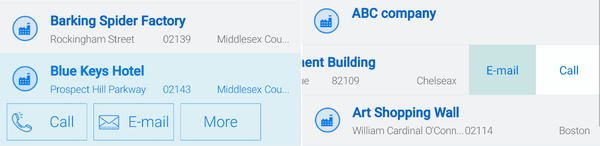
Buttons
You can add buttons to the view. Depending on your device, buttons are displayed when you select a record in the list, or when you swipe from the right.
On Windows apps, buttons are displayed when you select a record. On Android and iOS, the behavior is controlled by the parameter Use Legacy List Buttons (in Woodford Configuration).
To add buttons to the view, proceed as follows:
- Select Buttons from the toolbar to display the command editor.
- The right pane shows your available commands, the left pane shows commands in use. Add buttons from right to left.
- For some commands you can specify more details, for example, what child entity record to create or which status to set for the record. Select the command and click Properties.
- Save all changes and publish the project.
| Note | To use buttons like E-mail or Call, the email address or telephone number fields must be included in the view. Also, Formatting of the field has to set correctly. |
You can also define custom buttons:
- Select Buttons from the toolbar.
- Click New Command and enter an internal name of the command and a label, then click OK.
- Save the buttons editor and return to the view.
- Select Button Click from the toolbar.
- Using the rules editor, define an action that the button should perform.
Actions when multiple records are selected
Similar to buttons, you can define actions that are available when you select multiple records in your view. To use multi-selection in the app, tap and hold a record until the selection checkboxes appear, or use the lasso tool on map views. Multi-selection offers the following functions:
- Access configurable commands from the hamburger menu in the top right corner. For example, you can export the selected records, or delete them.
- Tap Sum in the bottom right corner to access statistics/aggregation functions.
- Tap Items in the bottom left corner to "select all" or "select none".
In Woodford, edit a view and click Multi Select to set up the available commands. The operation is similar to view buttons or Form commands. To see how it works, you can also check this webinar section. Webinar
You can define your own custom commands that perform actions that are not available when using built-in commands. The actions cannot be configured in Woodford, you can define them using JavaScript. See the MobileCRM.UI.EntityList.onCommand function for more information.
You can disable multi-selection in views completely using Woodford configuration: Allow Multi-select In Lists.
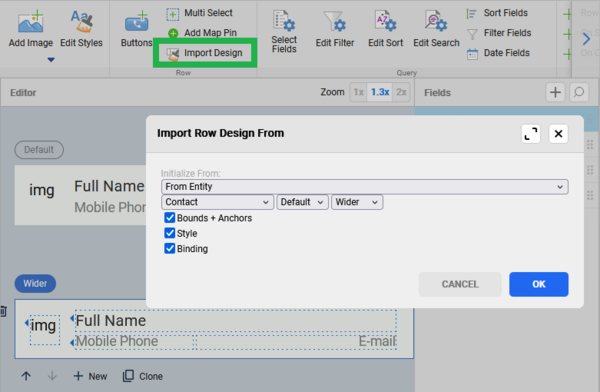
Import design
If you are creating custom view designs for your entities and you want to ensure that the design is consistent across the entire project, you can use the Import Design function. Select the entity, view, and row design that you want to use. You can either select one of your custom designs or a built-in design. You can also choose which parts of the view should be imported.
Sorting and filtering
Select fields
Click Select Fields to define which fields for the main entity, or even from related entities, should be available in the view. These fields are loaded from the database when the view is displayed. All fields that are displayed in the view must be loaded, but you can also load additional fields, for example, if you want to allow the user to filter the view according to these fields.
Edit filter
Edit Filter is used to restrict the displayed data in the view to only those that meet the specified conditions. Conditions are defined using the generic Filter editor user interface.
The difference between Sync Filters and view filters is that the Sync Filter controls which records from the backend make it to the offline database on the device, while the view filter determines which of the records available on the device are displayed in a particular view. This is the perspective of having more views for one entity.
Edit sort
Edit Sort allows you to select which field will be used for sorting and the direction of sorting (ascending or descending).
You can also sort by multiple fields.
Edit search
Click Edit Search to define where (in which field) will the application search for the character entered into the application’s search field. Also, it can be defined whether to search at the field’s beginning, end, or in each full text. You can add multiple fields, the conditions are combined using the logical operation OR.
Because the search uses OR, to enable more advanced search, you can create a filter with a condition over a text field (e.g. Name, Title etc.) and enter @@filter@@ as a filtered text. This will be replaced (in runtime) by the text entered into the search field on the view; see example.
Searching is generally fast, however, these are some of the factors that affect search speed:
- number of records in an entity where you search
- view filters with linked entities
- complexity of the database
- device performance (power)
- number of fields used in search
If you have fields for GPS coordinates in the entity, and if you enable this option for the mobile project, users will be able to switch the view from list to map; the records will be displayed on the map.
Sort fields and filter fields
Since version 9.1 of Mobile CRM app, you can set up additional sorting and filtering on view by using the Search bar. In these two view options, you can specify which fields are available to users for this additional sorting and filtering.
Calendar fields
Click Calendar Fields to customize how this view behaves on the Calendar.
- On the Dates tab, specify which fields are used as Start and End date fields.
- On the Cards tab, configure which details appear on the task card in Day or Week view. By default, only Header is shown, but you can add up to two more fields (maximum three).
Business logic
Resco mobile apps support custom business logic for adding advanced features to your views. Views support the following actions that trigger no-code scripts (rules). Rules are edited in the Rules_editor.
- Row Script – executed for each row when a view is loading or refreshing
- On Save – triggered by saving an Editable field
- On Change – triggered by changing an Editable field
- Button Click – triggered by tapping a view button
- Cell Click – triggered by tapping a cell
Iframes
You can use Offline HTML functionality to add JavaScript and JSBridge to views and perform validation; for example when you use the view to change the data (editable fields, MultiSelect), and to handle view buttons. It is also possible to use JavaScript and JSBridge to load records to the view (FetchXML). For more information about extending views by using this technology, please check the following part of a webinar. Webinar
There are additional validation options, like the possibility for the app to ask whether a change should be saved or discarded when users edit records on lists; OnChange and OnSave actions triggering in JavaScript, validations when records are modified or saved directly on a list, etc. can be seen in this webinar. Webinar
See Resco JavaScript Bridge for more information.
| Note | If you are using JavaScript to provide source data for a view, this applies to the default list view, but not to the map view. Map views and route plans use the original fetch in the view combined with the latitude and longitude of the area currently displayed on the map; custom data provided by JSBridge are ignored. |
Miscellaneous
Flipping between list, map, and chart
The traditional way of displaying records is as a list. If the records include location information, users can flip the view to a map. If the entity has a chart defined, users can flip to that as well.
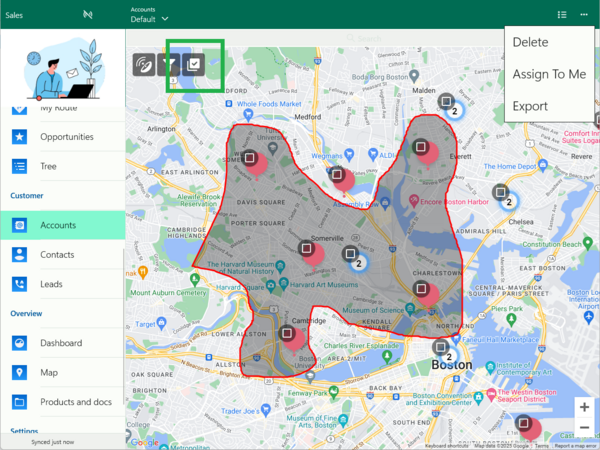
Map view
Records can be displayed on a map if they include geographic coordinates, i.e., latitude and longitude fields. Woodford comes with the Geocoding feature that can convert street addresses into latitude and longitude.
If you don't like the standard map pins, you can configure custom map pins, including the option to use different pins for different record types. If there are too many pins to fit into the map, you can enable map pin aggregation.
Users can tap any pin to display details about the record. Or they can use the lasso tool to select multiple records and perform bulk actions. Standard multi-select commands can be used directly from the map.
Best practice in renaming a view
Keep in mind that the view name is used as a logical name, so it's used all over the application. If someone changes the name of a view, it can cause issues with the application. Especially if they change the default view names on pre-defined entities.
Views are used in map, calendar, in entities as public, associated, or lookup views. So when the name is changed, you should reset the views on all these places.
It might be easier to use Localization feature to change the display name of a view, while keeping the logical name untouched. To enable this, you need to keep the view names without spaces or special characters. Underscore is okay to use, but the following characters are not: /\%#&*<>?|“+:{}. Also, some national characters and non-Latin characters are not allowed. See Localization examples for inspiration.
Editable field
Editable field, list, or editable grid is a feature that allows users to edit more records at once, directly from the view, without a need to go to edit form of a record.
To set a field to be editable directly in the view, set the field's Kind to one of the edit options:
- Edit: All changes to this kind of field must be saved. This requires that there's a Save button (only available in the public view - in the list of records accessed from the home screen).
- DirectEdit: Changes are changed immediately. This can be used also on lookup or associated views that don't have the Save button.
For more information about editable fields, please check this section of one of our webinars. Webinar The webinar is dated, but much of the information is still valid. One notable correction: editable views fully support validation using rules.
- Text-Edit versus Image-Edit
- Text-Edit and Text-DirectEdit can be used by cells with binding to any field that allows input, such as Text, Number, OptionSet, etc.
- Image-Edit and Image-DirectEdit can only be used on Image cells with binding to OptionSet field. In this case, the app lets users choose from a list of options. This is especially useful when you use images representing the status of a record. For example, you can represent the status of work orders by icon and let users change it by tapping the icon. Detailed example: Display "two options" as a checkbox on a view.
Clickable field
Clickable fields allow you to add a hyperlink of a lookup field to a view. When you tap the field, details of the lookup target record open. This can serve as a kind of a shortcut / quick access; for example to the parent account from an opportunity view.
To enable a clickable field on a view, set the field’s Kind to Text-Click or Image-Click.
Header
Enable Auto Header in the view properties to create a header row above the data rows. The header row allows simple sorting. This parameter affects your current view, but you can also configure the project-wide setting in Configuration, find Auto List Header under UI > List. To learn more, please check this part of a webinar. Webinar
If you need to include a custom label for one of the fields in the header, just like the city in the screen shot, you can use styles:
- Edit the view.
- Create a new style, for example "graycity", and assign it to the City field.
- Create a second style with the same name as above with the suffix "Header", i.e., "graycityHeader".
- Enter the custom label as Format string.
Tips:
- In project Configuration, this corresponds to the setting "Auto List Header".
- If you are using the associated list on a form, make sure to enable vertical scrolling (in the form property "Arrange items"). Horizontal scrolling disables headers.
This feature does not require setup in Woodford project. It allows to see some additional information when using multiselect in Resco Mobile CRM app, like number of selected items vs number of all items in the view or setting up the aggregation (e.g. sum of total amount on Opportunity) for selected vs all items in the view.
To learn more, please check this part of a webinar and this part to see it in action. Webinar
Display multiple records in one row
Traditionally, lists show one record per line. However, you can switch the Default layout property to "as Grid" if you want to display records in multiple columns.
Special views
Woodford offers two special views, one for searching, other for filtering. The following applies to special views.
- To create them, use the Special View button, not New View.
- Do not rename them; use the default names (SearchView and FilterView).
- Only one instance of each special view can exist for an entity.
Search view
It is possible to create a specific view used to display search results. The app automatically switches to this view when you are using the search box.
This needs to be a public view named exactly SearchView; it cannot be hidden. You can set up different looks and functionality of this view. To see it in action, please check this WEBINAR SECTION. Webinar
Filter view
Filter view is used when using an inline filter in a lookup form.
Private views
App users can create and manage their own custom views. See Private view for more information.
{{#CI form: title = Was this information helpful? How can we improve?
| type = inputs
| [textarea]
}}